ATLAS OF RADIOLOGICAL IMAGES v.1
General University Hospital and 1st Faculty of Medicine of Charles University in Prague
Cerebral hemorrhage, hypertonic hemorrhage, hemocephalus, subfalcine herniation, descendent transtentorial herniation
CASE
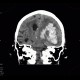
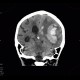
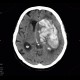
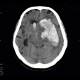
CT shows massive bleeding into the left frontal and parietal lobe which extended into the left and right lateral ventricles causing hemocephalus. The hemorrhage is surrounded by hypodense rim of edema and causes subfalcine herniation with severe shift of midline structures to the right. Note also that the left ambient cistern is obliterated which is a sign of transtentorial herniation.
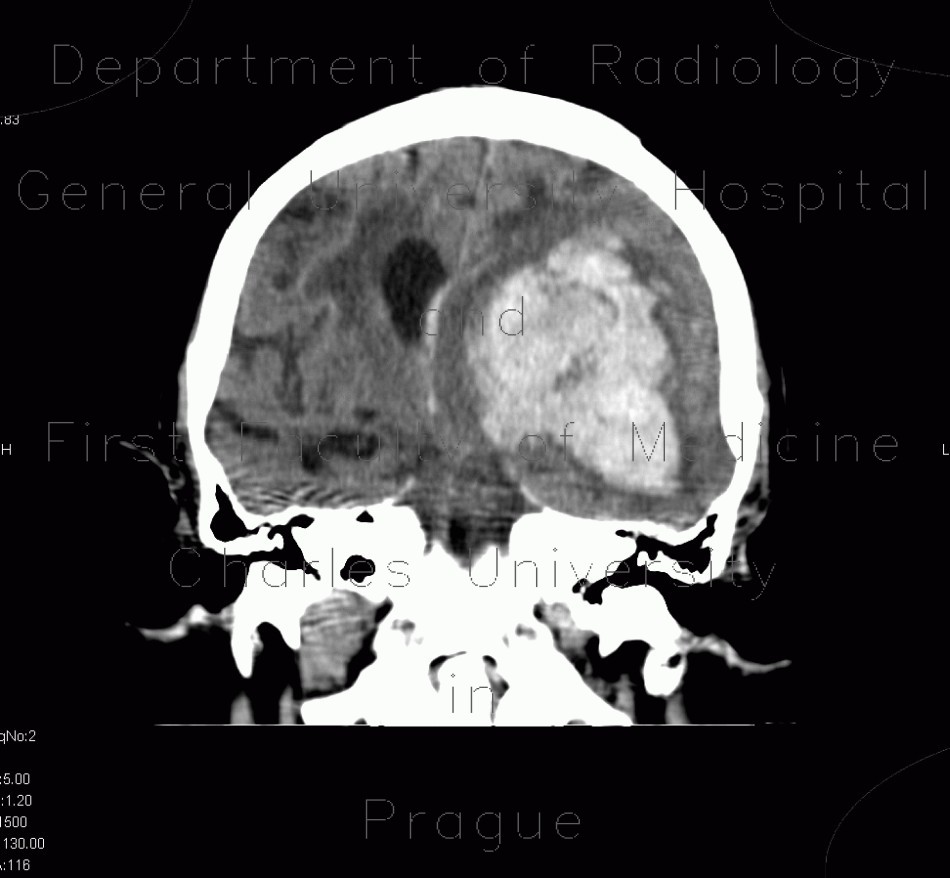
Cerebral hemorrhage, hypertonic hemorrhage, hemocephalus, subfalcine herniation, descendent transtentorial herniation (5738)