ATLAS OF RADIOLOGICAL IMAGES v.1
General University Hospital and 1st Faculty of Medicine of Charles University in Prague
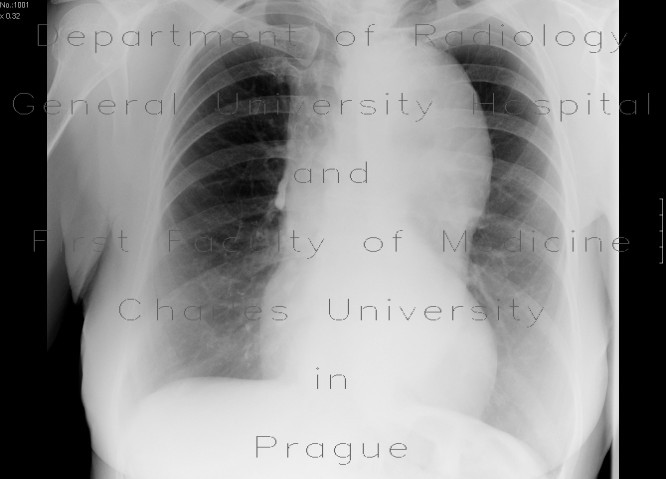
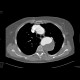
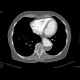
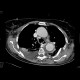
Dissecting aneurysm of the thoracic aorta, thrombosis of false lumen
CASE
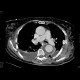
Two cases of aneurysmal dilatation of the thoracic aorta. Both of them affect the descending aorta (Stanford B). In the first case, it is an dissecting aneurysm, with false lumen (located posteriorly) being trombosed. In the second case, a fusiform aneurysm contains circular thrombosis.