ATLAS OF RADIOLOGICAL IMAGES v.1
General University Hospital and 1st Faculty of Medicine of Charles University in Prague
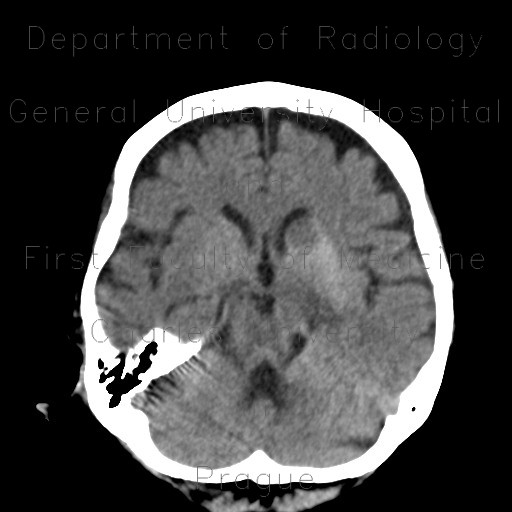
Infarction in basal ganglia, hemorrhagic transformation, follow-up
CASE
Images from the first study show that basal ganglia on both sides are edematous, enlarged and have increased density. This is a result of severe stenosis of internal carotid artery on the left side causing ischemia and hemorrhagic transformation. The follow-up study show, that the edema receded and so did the hyperdensity. The final result is a post-ischemic lacuna on the left and dilatation of the frontal horn of the left ventricle due to atrophy of basal ganglia, especially caput of the caudate nucleus.